Loading... # vector 容器的基本概念 <div class="tip inlineBlock share"> vector的数据安排以及操作方式,与array非常相似,两者的唯一差别在于空间的运用的灵活性。Array是静态空间,-旦配置了就不能改变,要换大一点或者小一点的空间,可以,-切琐碎得由自己来,首先配置-块新的空间,然后将旧空间的数据搬往新空间,再释放原来的空间。Vector 是动态空间,随着元素的加入,它的内部机制会自动扩充空间以容纳新元素。因此vector的运用对于内存的合理利用与运用的灵活性有很大的帮助,我们再也不必害怕空间不足而一开始就要求一 个大块头的array了。 Vector的实现技术,关键在于其对大小的控制以及重新配置时的数据移动效率,--旦vector旧空间满了,如果客 户每新增一一个元素, vector 内部只是扩充一个元素的空间,实为不智,因为所谓的扩充空间(不论多大),一如刚所说,是”配置新空间-数据移动-释放旧空间”的大工程,时间成本很高,应该加入某种未雨绸缪的考虑,稍后我们便可以看到vector的空间配置策略。 </div> 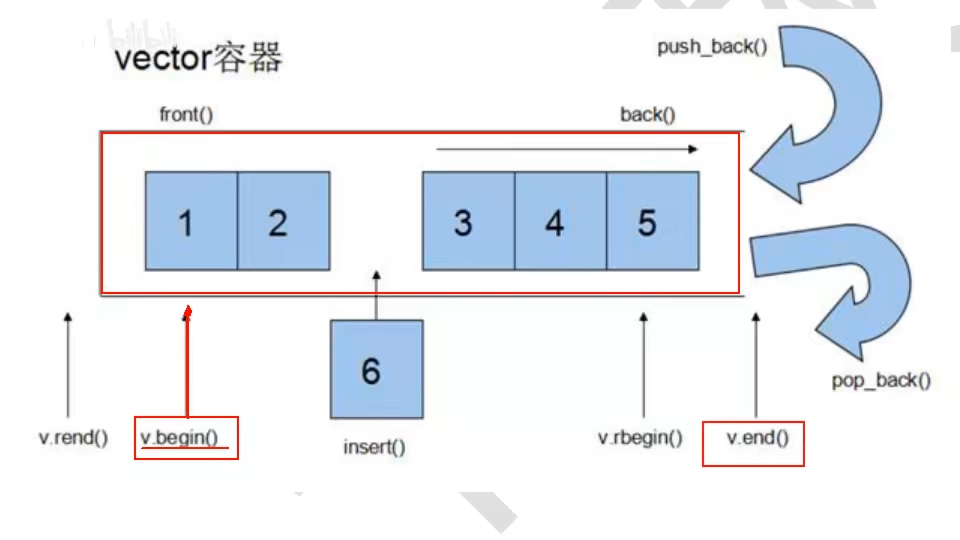 ## vector 迭代器 <div class="tip inlineBlock share"> Vector维护- -个线性空间,所以不论元素的型别如何,普通指针都可以作为vector的迭代器,因为vector迭代器 所需要的操作行为,如operaroe, operator->, operator+t, operator-, operator+, operator,operator+=,operator-=,普通指针天生具备。Vector支持随机存取,而普通指针正有着这样的能力。所以vector提供的是随机访问迭代器(RandomAccess Iterators). </div> * 根据上述描述,如果我们写如下的代码: ```C++ #include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; void print(int a) { cout << a << ' '; } int main() { vector<int> v; v.push_back(1); v.push_back(2); v.push_back(3); v.push_back(4); vector<int>::iterator it_start = v.begin(); vector<int>::reverse_iterator it_start1 = v.rbegin(); //这个迭代器++,是往前移动 for_each(it_start, v.end(), print); cout << endl; for_each(it_start1, v.rend(), print); return 0; } ``` ## vector 数据结构 <div class="tip inlineBlock share"> Vector所采用的数据结构非常简单,线性连续空间,它以两个迭代器Myfirst和Mylast分别指向配置得来的连续空间中目前已被使用的范围,并以迭代器_Myend指向整块连续内存空间的尾端。 为了降低空间配置时的速度成本,vector实际配置的大小可能比客户端需求大一些,以备将来可能的扩充,这边是容量的概念。换句话说,一个vector的容量永远大于或等于其大小,一旦容量等于大小,便是满载,下次再有新增元素,整个vector容器就得另觅居 </div> <div class="tip inlineBlock error"> 注意: 所谓动态增加大小,并不是再原空间之后续接新空间(应为无法保证原空间之后尚有可配置的空间),而是申请一块更大的内存空间,然后将原来的数据拷贝到新的空间,并释放原来的空间。因此,对vector的任何操作,一旦引起空间的重新配置,指向vector的所有迭代器都失效了,这是程序员容易犯的一个错误,务必小心。 </div> ## vector 常用API操作 ### 1、构造函数 > **<span style="color:#9932CC">vector的构造函数</span>** > vector<T> v; //采用模板实现类实现,默认构造函数 > vector(v.begin(), v.end());//将v[begin(), end())区间中的元素拷贝给本身。 > vector(n, elem);//构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。 > vector(const vector &vec);//拷贝构造函数。 ```C++ #include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; void print(int a) { cout << a << " "; } int main() { int i; vector<int> v1; for (i = 1; i <= 100; i++) v1.push_back(i); //一、vector(v.begin(), v.end());//将v[begin(), end())区间中的元素拷贝给本身。 vector<int> v2(v1.begin(), v1.end()); vector<int> v3(v1.begin()+2, v1.end()-3); //输出v2 vector<int>::iterator it = v2.begin(); vector<int>::reverse_iterator it1 = v2.rbegin(); for_each(it, v2.end(), print); cout << endl << endl << endl << endl; for_each(it1, v2.rend(), print); cout << endl << endl << endl << endl; cout << endl << endl << endl << endl; cout << endl << endl << endl << endl; //输出v3 it = v3.begin(); it1 = v3.rbegin(); for_each(it, v3.end(), print); cout << endl << endl << endl << endl; for_each(it1, v3.rend(), print); cout << endl << endl << endl << endl; //二、vector(n, elem);//构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。 vector<int> v4(15, 6); it = v4.begin(); for_each(it, v4.end(), print); return 0; } ``` ### 2、赋值操作 > assign(beg, end);//将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。 > assign(n, elem);//将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。 > vector& operator=(const vector &vec);//重载等号操作符 > swap(vec);// 将vec与本身的元素互换。//两个指针交换位置 ```C++ #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; void print(int a) { cout << a << " "; } int main() { int i; vector<int> v1; for (i = 1; i <= 20; i++) { v1.push_back(i); } //一、assign(beg, end);//将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。 vector<int> v2; v2.assign(v1.begin(), v1.end()); vector<int>::iterator it = v2.begin(); cout << "v2 = "; for_each(it, v2.end(), print); cout << endl; //二、vector& operator=(const vector &vec);//重载等号操作符 vector<int> v3; v3 = v1; it = v3.begin(); cout << "v3 = "; for_each(it, v3.end(), print); cout << endl; //三、assign(n, elem);//将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。 vector<int> v4; v4.assign(15, 1); it = v4.begin(); cout << "v4 = "; for_each(it, v4.end(), print); cout << endl; //四、swap(vec);// 将vec与本身的元素互换。 vector<int> v5; for (i = 100; i <= 120; i++) { v5.push_back(i); } it = v5.begin(); cout << "v5 = "; for_each(it, v5.end(), print); cout << endl; v5.swap(v2); cout << "v5.swap(v2):\n"; //输出看结果 it = v2.begin(); cout << "v2 = "; for_each(it, v2.end(), print); cout << endl; it = v5.begin(); cout << "v5 = "; for_each(it, v5.end(), print); cout << endl; return 0; } ``` ### 2、大小操作 > size();//返回容器中元素的个数 > empty();//判断容器是否为空 > resize(int num);//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。 > resize(int num, elem);//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长>度的元素被删除。 > capacity();//容器的容量 > reserve(int len);//容器预留len个元素长度,预留位置不初始化,元素不可访问。 ```C++ #include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; void print(int a) { cout << a << ' '; } int main() { int i; vector<int> v1; for (i = 1; i <= 20; i++) { v1.push_back(i); } vector<int>::iterator it = v1.begin(); cout << "v1 = "; for_each(it, v1.end(), print); //一、size();//返回容器中元素的个数 cout << "v1.size() = "; cout << v1.size() << endl; //二、capacity();//容器的容量 cout << "v1.capacity() = "; cout << v1.capacity() << endl; //三、empty();//判断容器是否为空 if (!v1.empty()) { cout << "不为空" << endl; } //四、resize(int num);//重新指定容器的长度为num。 //若容器变长,则以默认值(默认值是0,可以输入第二个参数为默认值)填充新位置。 //如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。 v1.resize(10); it = v1.begin(); cout << "v1.resize(10) = "; for_each(it, v1.end(), print); cout << endl; //五、resize(int num, elem);//重新指定容器的长度为num, //若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长>度的元素被删除 v1.resize(30, 8); it = v1.begin(); cout << "v1.resize(30,8) = "; for_each(it, v1.end(), print); cout << endl; //六、reserve(int len);//容器预留len个元素长度,预留位置不初始化,元素不可访问。 vector<int> v2; v2.reserve(1000); cout << "v2.size() = "; cout << v2.size() << endl; cout << "v2.capacity() = "; cout << v2.capacity() << endl; return 0; } ``` 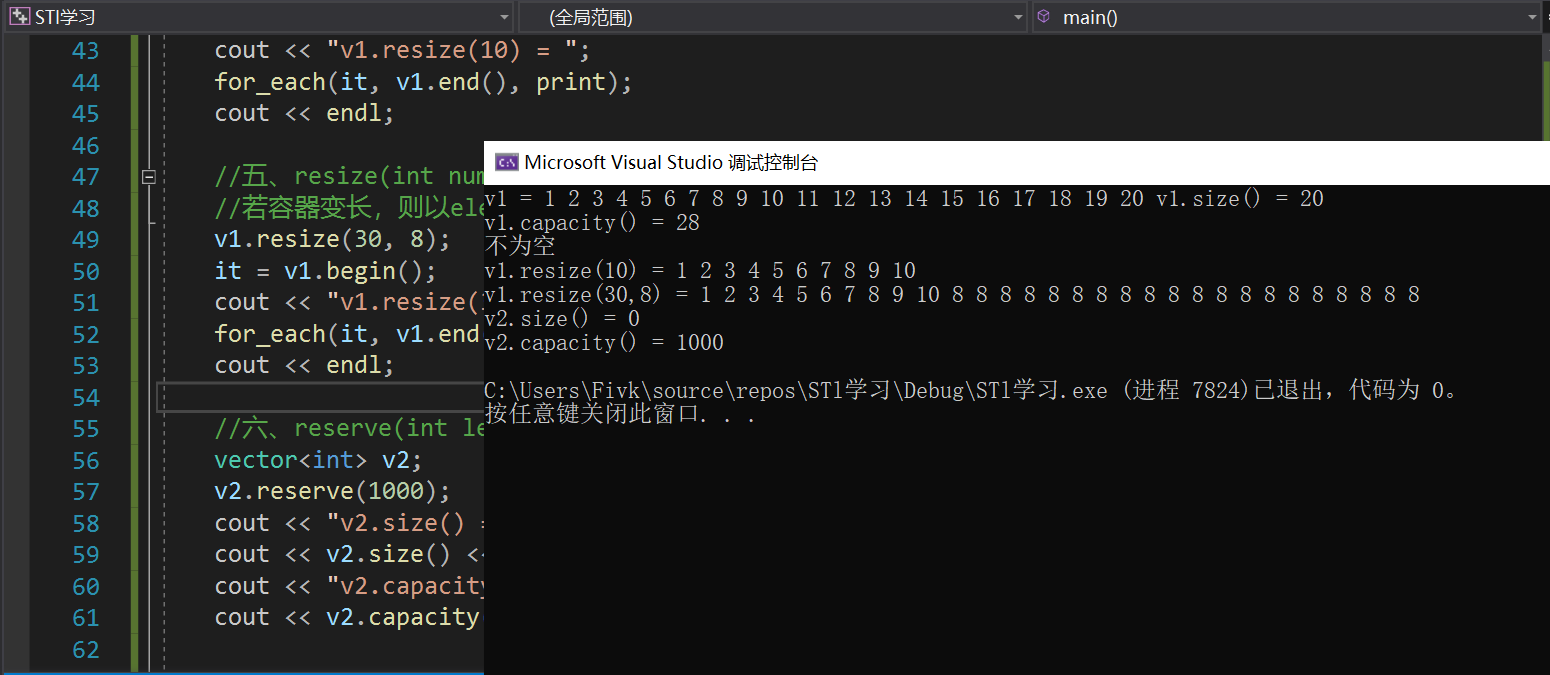 ### 3、数据存取操作 > at(int idx); //返回索引idx所指的数据,如果idx越界,抛出out_of_range异常。 > operator[];//返回索引idx所指的数据,越界时,运行直接报错 > front();//返回容器中第一个数据元素 > back();//返回容器中最后一个数据元素 ```C++ #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; void print(int a) { cout << a << ' '; } int main() { int i; vector<int> v1; for (i = 1; i <= 20; i++) { v1.push_back(i); } vector<int>::iterator it = v1.begin(); cout << "v1 = "; for_each(it, v1.end(), print); cout << endl; //一、at(int idx); //返回索引idx所指的数据,如果idx越界,抛出out_of_range异常。 cout << "v1.at(2) = " << v1.at(2) << endl; //二、operator[];//返回索引idx所指的数据,越界时,运行直接报错 cout << "v1[2] = " << v1[2] << endl; //三、front();//返回容器中第一个数据元素 cout << "v1.front() = " << v1.front() << endl; //四、back();//返回容器中最后一个数据元素 cout << "v1.back() = " << v1.back() << endl; return 0; } ``` 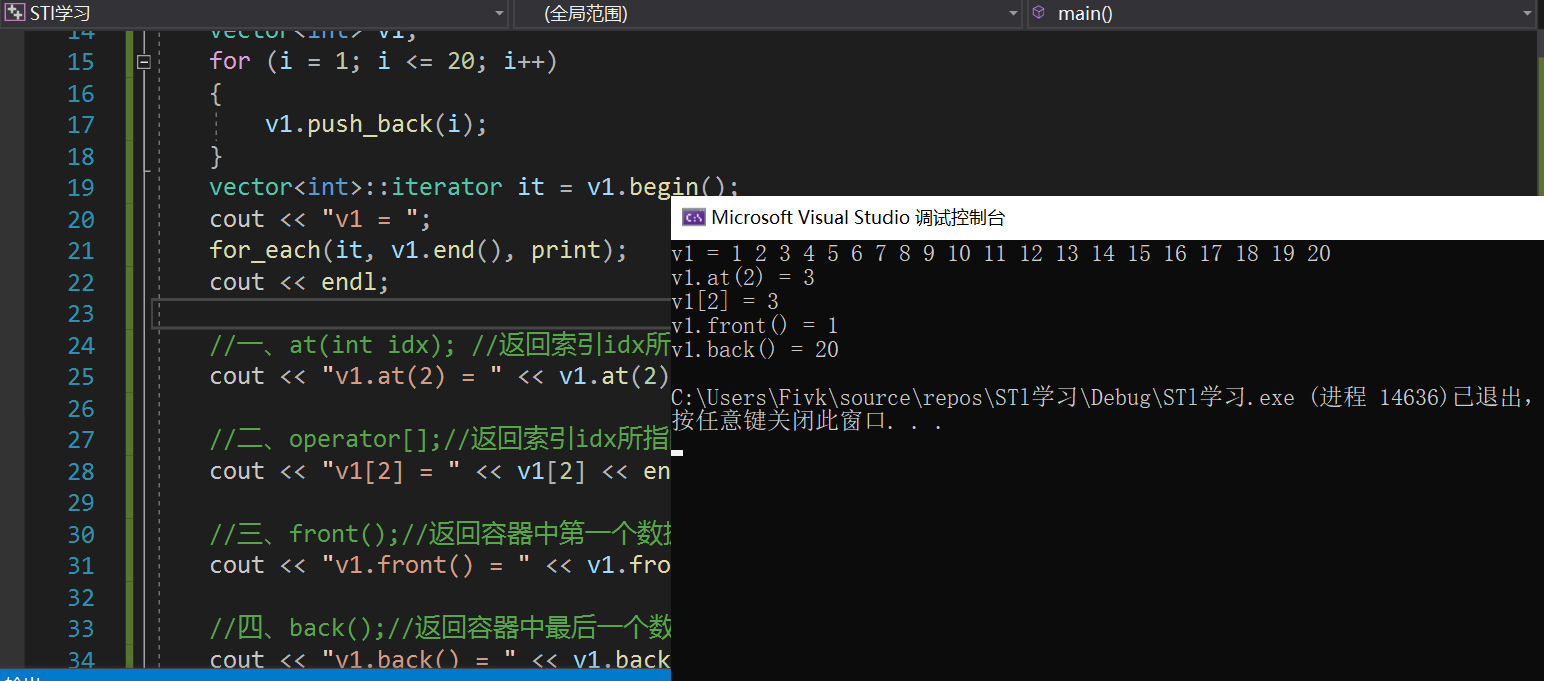 ### 4、插入和删除操作 > insert(const_iterator pos, int count,ele);//迭代器指向位置pos插入count个元素ele. > push_back(ele); //尾部插入元素ele > pop_back();//删除最后一个元素 > erase(const_iterator start, const_iterator end);//删除迭代器从start到end之间的元素 > erase(const_iterator pos);//删除迭代器指向的元素 > clear();//删除容器中所有元素 ```C++ #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; void print(int a) { cout << a << ' '; } int main() { int i; vector<int> v1; for (i = 1; i <= 20; i++) { v1.push_back(i); } vector<int>::iterator it = v1.begin(); cout << "v1 = "; for_each(it, v1.end(), print); cout << endl; //一、insert(const_iterator pos, int count,ele);//迭代器指向位置pos插入count个元素ele. v1.insert(v1.begin() + 3, 10, 0); cout << "v1.insert(v1.begin() + 3, 10, 0) = "; it = v1.begin(); cout << "v1 = "; for_each(it, v1.end(), print); cout << endl; //二、push_back(ele); //尾部插入元素ele v1.push_back(1000); cout << "v1.push_back(1000) = "; it = v1.begin(); cout << "v1 = "; for_each(it, v1.end(), print); cout << endl; //三、pop_back();//删除最后一个元素 v1.pop_back(); cout << "v1.pop_back() = "; it = v1.begin(); cout << "v1 = "; for_each(it, v1.end(), print); cout << endl; //四、erase(const_iterator start, const_iterator end);//删除迭代器从start到end之间的元素 v1.erase(v1.begin() + 3, v1.begin() + 10 + 3); cout << "v1.erase(v1.begin() + 3, v1.begin() + 10 + 3) = "; it = v1.begin(); cout << "v1 = "; for_each(it, v1.end(), print); cout << endl; //五、erase(const_iterator pos);//删除迭代器指向的元素 v1.erase(v1.begin() + 3); cout << "v1.erase(v1.begin() + 3) = "; it = v1.begin(); cout << "v1 = "; for_each(it, v1.end(), print); cout << endl; //六、clear();//删除容器中所有元素(不代表释放容器) v1.clear(); cout << "v1.erase(v1.begin() + 3) = "; it = v1.begin(); cout << "v1 = "; for_each(it, v1.end(), print); cout << endl; return 0; } ``` 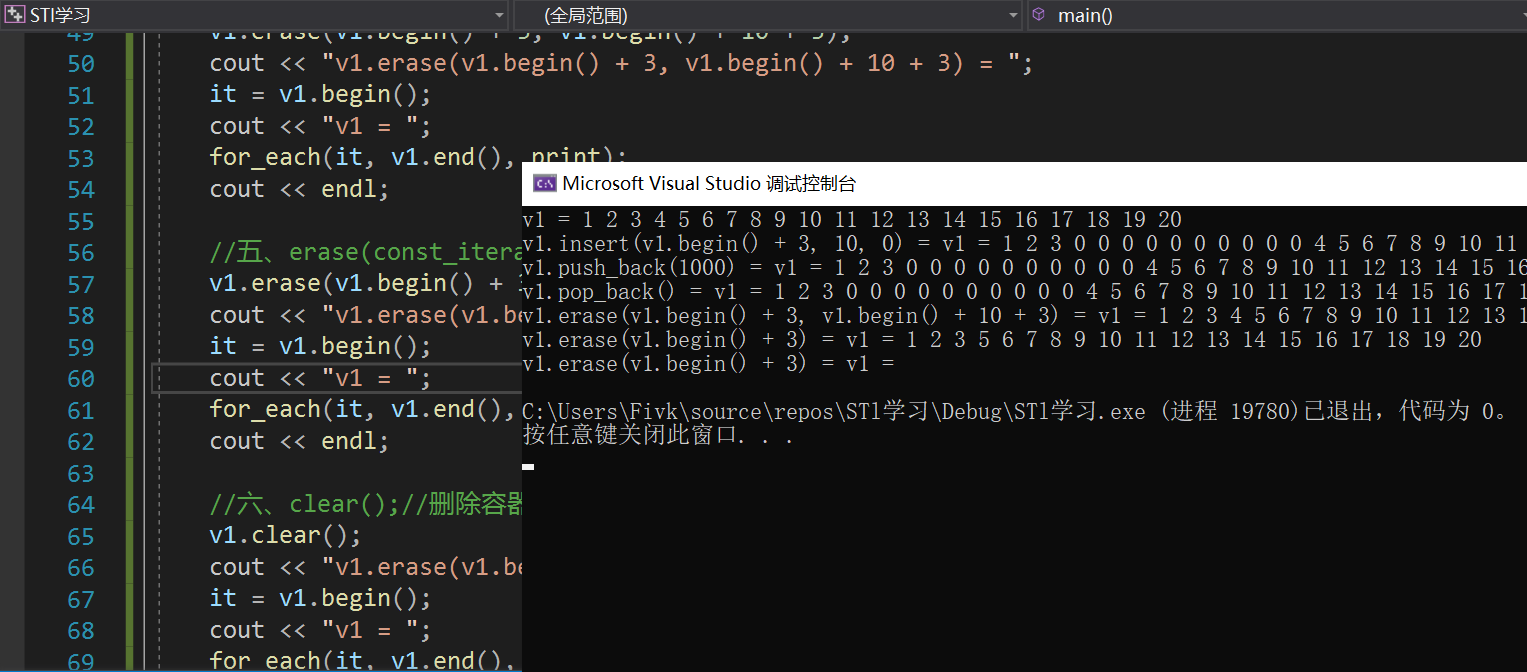 ### 5、swap收缩空间 ```C++ #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; void print(int a) { cout << a << ' '; } int main() { int i; vector<int> v1; for (i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) { v1.push_back(i); } vector<int>::iterator it = v1.begin(); cout << "v1 = "; // for_each(it, v1.end(), print); // cout << endl; //size();//返回容器中元素的个数 cout << "v1.size() = "; cout << v1.size() << endl; //capacity();//容器的容量 cout << "v1.capacity() = "; cout << v1.capacity() << endl; //我们现在不要10000了,我们现在只要10 v1.resize(10); cout << "v1.resize(10):" << endl; //size();//返回容器中元素的个数 cout << "v1.size() = "; cout << v1.size() << endl; //capacity();//容器的容量 cout << "v1.capacity() = "; cout << v1.capacity() << endl; cout << "我们发现,size后,元素变为10个,但是capacity容量还是占了这么多。" << endl; cout << "所以我们需要使用swap回收空间" << endl; vector<int>(v1).swap(v1); cout << "vector<int>(v1).swap(v1) :" << endl; //size();//返回容器中元素的个数 cout << "v1.size() = "; cout << v1.size() << endl; //capacity();//容器的容量 cout << "v1.capacity() = "; cout << v1.capacity() << endl; cout << "现在就释放了多余的容量" << endl; return 0; } ``` 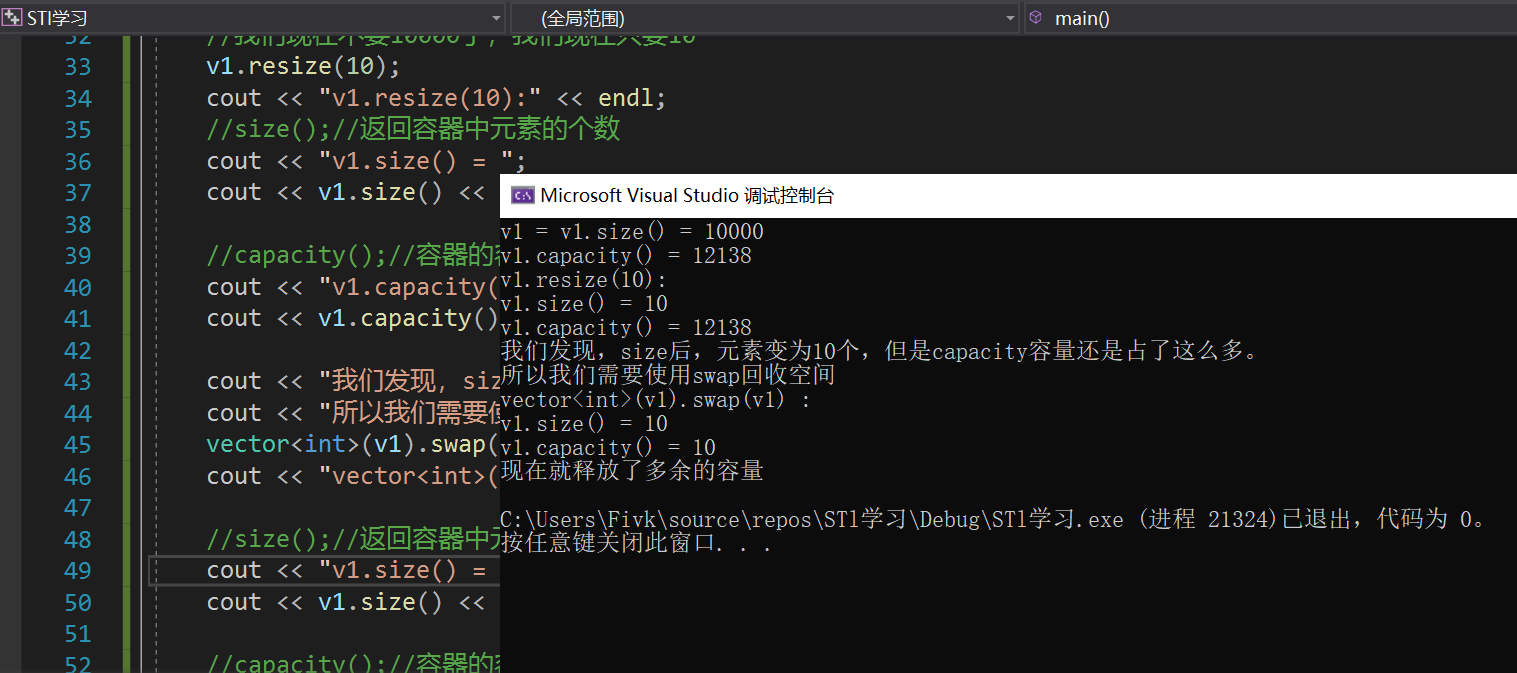 <div class="tip inlineBlock warning"> 通过上面代码,我们释放了多余的容量。那么内部是怎么实现的呢? </div> 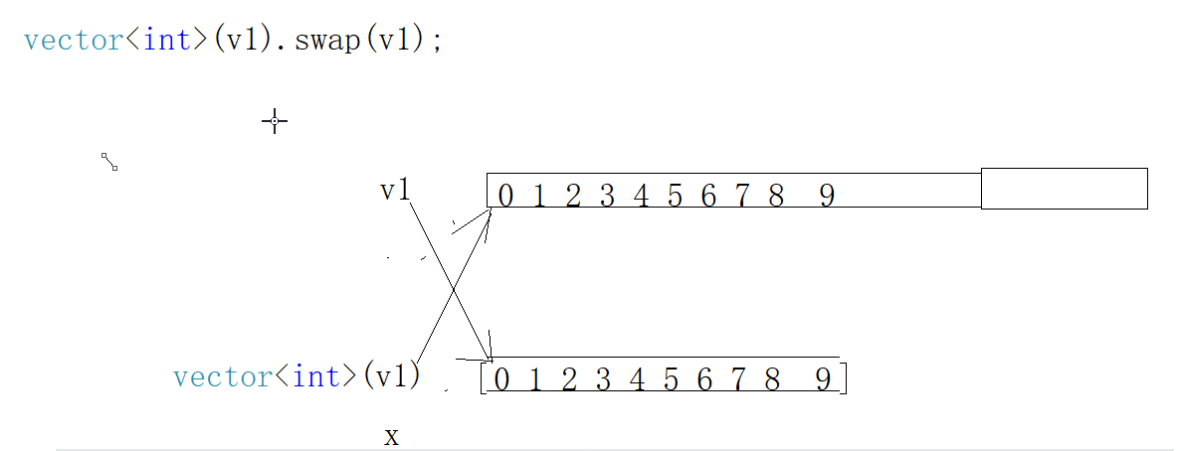 <iframe class="iframe_video" src="//player.bilibili.com/player.html?aid=625879966&bvid=BV1Pt4y1y7yU&cid=197536284&page=28" scrolling="no" border="0" frameborder="no" framespacing="0" allowfullscreen="true"> </iframe> > 直接到视频6分钟 ### 利用 reserve 预留空间 和 指针 计算重新开辟了多少次空间 ```C++ #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; void print(int a) { cout << a << ' '; } int main() { int i, count = 0; vector<int> v1; int* p = NULL; for (i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) { v1.push_back(i); if (p != &v1[0]) { count++; p = &v1[0]; } } cout << count; return 0; } ``` ### 使用sort排序容器 ```C++ #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> using namespace std; class Person { public: Person(int age, string s) { this->age = age; this->name = s; } int age; string name; }; void print(int a) { cout << a << ' '; } void print_Person(Person& a) { cout << a.name << ' ' << ':' << a.age << endl; } bool cmp(int a, int b) { return a > b;//a > b 的结果是0或1 //如果返回true 则a的优先级高 //如果返回false 则b的优先级高 } bool cmp_Person(Person a, Person b) { return a.age > b.age; } int main() { int i; vector<int> v1; v1.push_back(4); v1.push_back(2); v1.push_back(8); v1.push_back(5); sort(v1.begin(), v1.end(), cmp);//排序int类型 vector<int>::iterator it = v1.begin(); for_each(it, v1.end(), print); //下面我们排序自定义类型 vector<Person> v2; Person p1(10, "安琪拉"); Person p2(12, "小乔"); Person p3(13, "武则天"); Person p4(13, "上官婉儿"); Person p5(9, "王昭君"); Person p6(15, "不知火舞"); v2.push_back(p1); v2.push_back(p2); v2.push_back(p3); v2.push_back(p4); v2.push_back(p5); vector<Person>::iterator it_Person = v2.begin(); cout << endl; sort(v2.begin(), v2.end(), cmp_Person); for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print_Person); return 0; } ``` 最后修改:2021 年 04 月 14 日 © 禁止转载 打赏 赞赏作者 支付宝微信 赞 如果觉得我的文章对你有用,请随意赞赏